First, data non-dependent acquisition ( DIA )
With the rapid development of life sciences, the focus and research trends of proteomics have gradually shifted from qualitative to quantitative. Quantitative proteomics is the analysis of protein expression and differences in cells, tissues and even intact organisms. It is of great significance for the exploration of biological process mechanisms and the discovery and verification of clinical diagnostic markers.
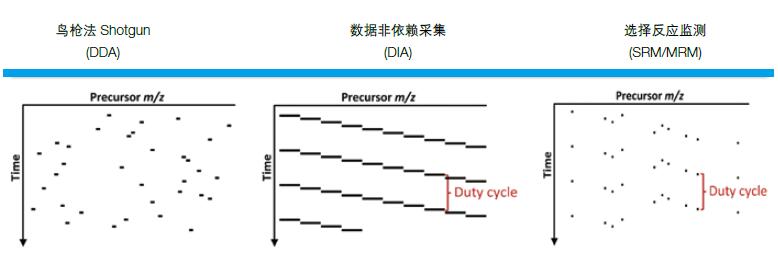
Data Independent Acquisition (DIA) based on the electrostatic field orbitrap Orbitrap is a new, holographic mass spectrometry technology that Thermo Scientific brings to users. DIA divides the entire full scan range of the mass spectrum into several windows, and selects, fragments, and detects all ions in each window at high speed and cyclically, so that all pieces of information of all ions in the sample are obtained without any omission and difference. figure 1).
Figure 1. Comparison of DIA and classic Shotgun, SRM/MRM
Compared with the traditional proteomics "Shotgun", DIA: (1) obtains information on all peptides without discrimination, does not cause loss of low-abundance protein information, (2) fixed cycle time, scan points Uniform, high quantitative accuracy, (3) The choice of peptides is not random, the data can be traced back, and it has better reproducibility for complex protein samples, especially low-abundance proteins. Compared with traditional mass spectrometry quantitative “gold standard†selective reaction monitoring/multi-reaction monitoring (SRM/MRM), DIA: (1) no need to specify the target peptide in advance, suitable for unknown protein analysis; (2) no optimization method, data acquisition Then, based on the spectral library, qualitative confirmation and quantitative ion screening are realized; (3) There is no upper limit of flux, which is suitable for quantitative analysis of large-scale proteins.
To put it bluntly, Shotgun is like a machine gun that strikes as many targets as possible efficiently; SRM/MRM is like a precision sniper that strikes a specific target with accuracy; and DIA is like a carpet bombing that strikes all targets without fail ( figure 2).
Figure 2. Comparison of features of Shotgun, DIA, and SRM/MRM
DIA effectively combines the advantages and features of Shotgun and SRM/MRM to bring users a new mass spectrometry experience and a powerful proteomics quantification strategy. In clinical research, high complexity, large sample size, and sample instability are difficult to analyze, and DIA provides a uniform, undifferentiated mass spectrometry acquisition method that can be used when the sample information is “completely unknownâ€. High-throughput, high-speed acquisition of samples, and in-depth analysis and mining after obtaining data, is a tool for clinical proteomics experiments. In biological research, the trend of protein expression at multiple time points or conditions is the focus of analysis, and the sensitivity, precision and reproducibility of DIA provide a strong guarantee for accurate and reliable quantitative results.
1. DIA
DIA usually splits the full scan range of m/z 400–1200 into 25 m/z windows (32 windows total), in order (m/z 400-425, m/z 425-450, ..., m/z) 1175-1200) Select and fragment all the ions in the window, and detect all the fragments generated by the ions in the window. 32 secondary spectra are obtained in one cycle and continuously collected cyclically (Fig. 3).
Figure 3. DIA acquisition principle
Orbitrap's ultra-high resolution (_ 140,000), ultra-fast scanning speed (32–64 ms), and ultra-high sensitivity (amol level) make DIA more user-friendly than other similar technologies such as SWATH. A better performance experience. In addition, Orbitrap's flexible and versatile acquisition methods provide users with more flexible method settings: (1) use narrower selection windows (eg 20 m/z) or asymmetric windows (at the peak) depending on the complexity of the sample Intensive range uses a narrower selection window) for better selectivity; (2) Adjust ion implantation time and resolution based on the signal intensity of the peptide to achieve higher sensitivity; (3) Use for large sample sizes Fast scanning speed and shorter gradient, further improve the efficiency of analysis; (4) Add a first-level full scan, collect the fragmentation while obtaining the parent ion information, and achieve more accurate qualitative and quantitative.
2. msxDIA
In addition to providing ultra-high resolution, ultra-fast scanning speed and ultra-high sensitivity analysis performance, Orbitrap's ultra-high resolution mass spectrometry has advanced design concepts that make it impossible for any other mass spectrometer to be realized - Multiple Accumulation Technology (Multiplexing) , msx). Combine multiple accumulation technologies with DIA to create a unique msxDIA that further reduces DIA's selection window and improves DIA's selectivity.
MsxDIA randomly selects 5 4 m/z windows (or 2 10 m/z windows) in turn, fragments, and accumulates them together, and finally injects Orbitrap to scan for 5 4 m/z windows (or 2 10) Spectra of all fragmentation information in the m/z window), then randomly select another 5 4 m/z windows (or 2 10 m/z windows) to analyze and continue until the entire full scan range is covered. The msxDIA total step size is 20 m/z, which does not affect the scanning speed. The 20 m/z consists of 5 segments (or 2 segments) of independent windows, objectively reducing the selection window to only 4 m/z (or 10 m). /z window). Figure 4 shows the principle of msxDIA in the 2 x 10 m/z mode.
Figure 4. The msxDIA acquisition principle (2 x 10 m/z mode)
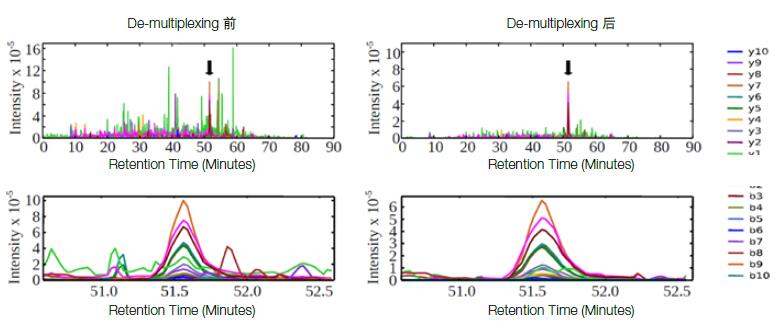
The data collected by msxDIA can be de-multiplexed using Skyline software to assign each fragment and response strength to a specific window, achieving selectivity comparable to Shotgun and SRM/MRM, minimizing co-elution. Interference between peptides and impurities (Figure 5). msxDIA is Orbitrap's unique new scanning technology, first developed by Skyline's developer, the University of Washington's MacCoss professor, and published in the journal Nature Method (Nat. Methods, 2013, 10(8): 744-746 ).
Figure 5. Comparison of msxDIA before and after multiple accumulation
Second, characteristics and advantages
Data non-dependent acquisition ( DIA ):
• Collect all ion and fragment spectra without losing any information and reproducible;
• Data is easy to trace, and even if no protein/compound can be found at current levels, it can be traced back in the future;
• No need to optimize the method, for the easy degradation of the sample can be collected immediately, after obtaining the data and then digging deep;
• Quantitative based on fragment ions (ie mother and child ion pairs) with good selectivity, comparable to SRM/MRM;
• The cycle time is fixed, the number of scanning points is uniform, and the quantitative accuracy is high;
• There is no upper limit for flux while monitoring all target proteins/compounds;
• Quantitative differentiation and discrimination of different post-translational modification sites for the same peptide.
Based on the data acquired non-dependent Orbitrap (DIA):
• Typically 35,000–60,000 resolution acquisition, high accuracy for qualitative and quantitative quantification of complex samples;
â—† Q-TOF DIA* acquisition resolution is about 20,000
• The quality axis is stable at 1 ppm for a long time, without internal standard calibration or frequent external standard calibration, the data is more assured and the flux is higher;
â—† Q-TOF DIA* acquisition requires internal standard calibration or frequent external standard calibration
• Amol (10-18 mol) grade with high sensitivity and high spectral quality;
â—† Q-TOF DIA* low acquisition sensitivity
• Ultra-fast scanning speed of 12–20 Hz while maintaining a high sensitivity of amol level;
â—† Q-TOF DIA* acquisition increases scanning speed and loses sensitivity
• Dynamic range and linear range of more than 5 orders of magnitude;
â—† Q-TOF DIA* acquisition dynamic range is 3~4 orders of magnitude
• Unique multi-accumulation msxDIA to further increase selectivity;
â—† Q-TOF DIA* does not have this function
• Flexible scanning capabilities for unique DIA modes such as pSMART and WiSIM.
â—† Q-TOF DIA* scanning mode single
*: Here DIA refers to the "Sequential Window Acquisition Trough High-resolution" technology developed by Ruedi Aebersold (Mol. Cell. Proteomics, 2012, 11(6): O111.016717)
Third, the workflow
Thermo Fisher Scientific's Orbitrap-based data-independent acquisition (DIA) solution, workflow (Figure 6) unified, proven, easy to use, high-throughput protein for any complex biological sample and clinical sample Quantitative analysis of histology.
The Orbitrap-based DIA solution is divided into three steps: First, the sample pre-processing is exactly the same as the classic Shotgun process. The sample is subjected to protein extraction, enzymatic hydrolysis, desalting, and then subjected to specific separation, enrichment and purification as needed. Direct injection analysis, or injection of mixed peptides before injection analysis (retention time correction); then, without prior knowledge of the sample information, directly using the unified DIA template, you can quickly and high-throughput Orbitrap mass spectrometry acquisition High-quality DIA data; finally, DIA data is scored using the authoritative Skyline software and spectral library matching to obtain credible identification results, and automatically select the most responsive and most selective ion ions for ion pair peak extraction. Get accurate quantitative information.
Figure 6. Orbitrap-based data-independent acquisition (DIA) solution
Fourth, Q Exactive series Orbitrap mass spectrometer
Electrostatic field orbitrap Orbitrap ultra high resolution mass analyzer
The Orbitrap, an electrostatic field orbital trap based on the Fourier transform principle, is the only mass analyzer based on a new theory in 30 years. It combines excellent performances such as ultra-high resolution, ultra-high-quality precision and ultra-high sensitivity, and has an extremely stable mass axis. The advantages of simple operation and maintenance and low cost of use. Since the first commercial Orbitrap mass spectrometer was launched in 2005, the development of high-level scientific research represented by proteomics has been greatly promoted, and it has quickly become the only gold standard for proteomics research. According to statistics, in recent years, the number of papers published by Orbitrap in high-level journals such as Nature, Science, and Cell is three times the sum of papers published by all other high-resolution mass spectrometers, and has become a tool for cutting-edge scientific research (Figure 7).
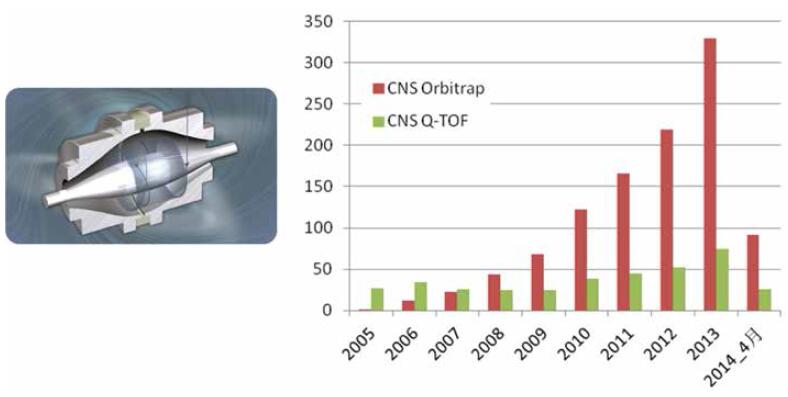
Figure 7. Trends in Orbitrap structure diagrams and published high-level papers
Figure 8. A tool for quantitative analysis - Q Exactive Series Ultra High Resolution Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer
Five, method settings and data collection
1. DIA
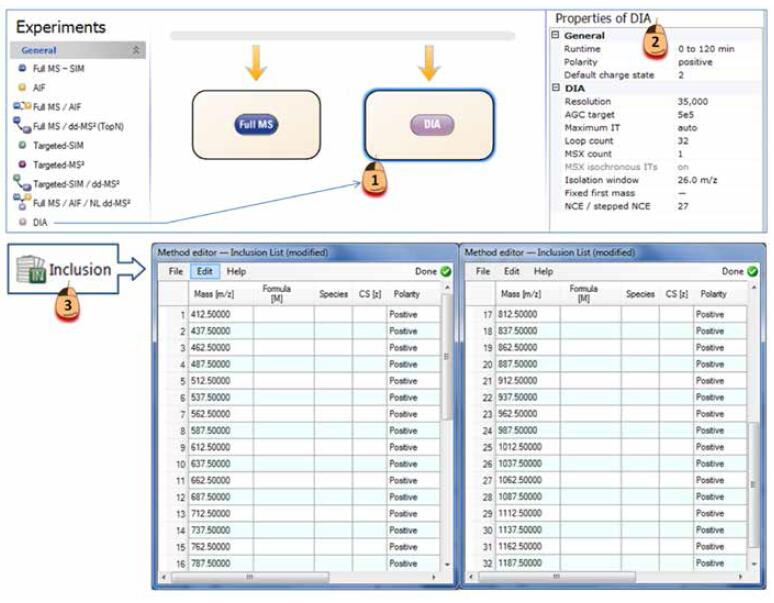
Q Exactive's DIA method is easy to edit, easy to use, and the process is straightforward, without any DIA analysis experience. All method settings can be completed in just three steps (Figure 9): (1) Drag the DIA module into the method flow in the template (if you add a level scan, drag the Full Mass module in front of the DIA module); (2) Modify the resolution (usually set to 35000) and window width in the DIA module as needed (if the actual window step size is 25 m/z, set 26 m/z, more than 1 m/z for Overlap between windows); (3 The Inclusion List generates the median value (m/z) of each window as the target. The method of saving after three steps is completed, and sample data collection is started immediately.
Figure 9. Three-step completion of DIA method editing
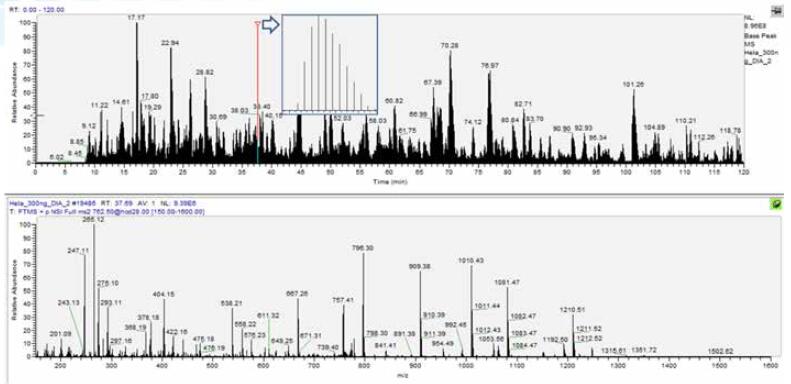
The typical DIA data is shown in Figure 10. From the chromatogram, the DIA data is not significantly different from the traditional Shotgun data, except that the number of secondary spectra per cycle is fixed, so the scan points are evenly distributed.
Figure 10. Typical DIA data
Figure 11. Four-step completion of the msxDIA method edit
2. msxDIA
Orbitrap's unique msxDIA method settings are equally easy to use, with just one more random Inclusion list generation (Figure 11): (1) Drag the DIA module into the method flow in the template (if you add a level 1 scan, it is in front of the DIA module Drag into the Full Mass module); (2) Take 2 x 10 m/z as an example, the MSX count in the DIA module is set to 2, and the window width is set to 10 m/z, that is, the 2 x 10 m/z mode parameter setting is completed. (3) Use the Skyline software to generate a random Inclusion list table; (4) Import the random Inclusion list table into the Inclusion list of the method, complete the method settings, and immediately start msxDIA data collection.
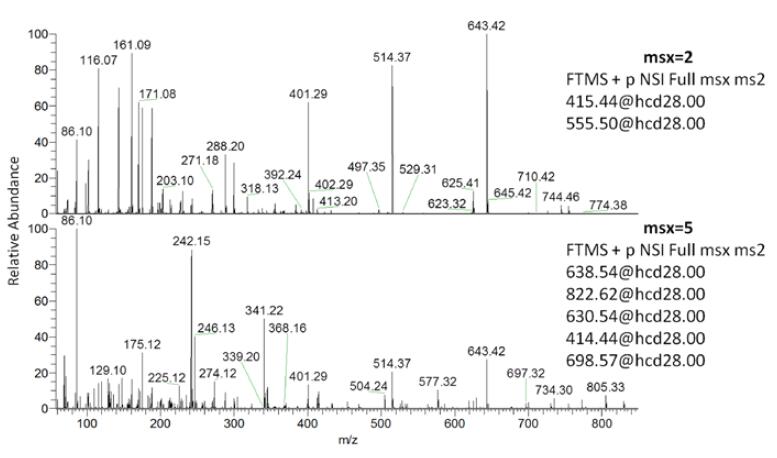
A typical msxDIA secondary mass spectrum is shown in Figure 12, and each spectrum contains fragmentation information for 2 (2 x 10 m/z mode) or 5 (5 x 4 m/z mode) windows, ie one scan acquisition 2 For one or five windows, the analysis efficiency is significantly improved, and the selectivity is also significantly improved due to window shrinkage.
Figure 12. Typical msxDIA secondary mass spectrum
Sixth, data analysis
DIA/SWATH data is complex and informative, so efficient and reliable data analysis and information mining is the bottleneck of DIA/SWATH analysis.
Skyline software
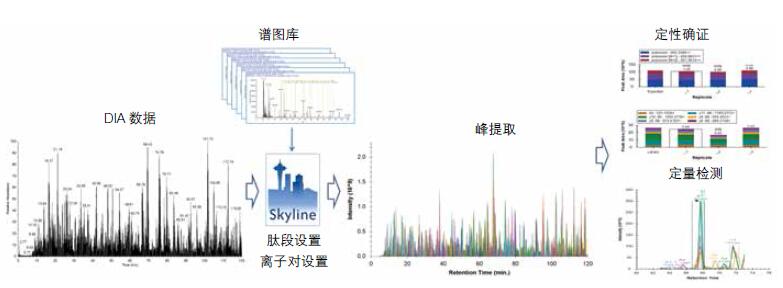
Skyline software is the target proteomics analysis software developed by the University of Washington's MacCoss laboratory (https://skyline.gs.washington.edu), the authoritative tool for DIA/SWATH data processing, and is widely used due to its comprehensive capabilities and powerful performance. Recognized, it is currently the most widely used DIA/SWATH parsing software. Working closely with Thermo Fisher Scientific, the MacCoss Professor Lab has optimized Skyline's processing of Orbitrap data, enabling a complete DIA analysis process from raw data to final results in one step, making Orbitrap DIA even more powerful.
Proteome Discoverer software (or MaxQuant, Mascot, etc.) search results for the library, import Skyline software; set the peptide, ion pair selection rules; select the qualified peptides and product ions from the spectrum to generate Target List; import DIA/msxDIA data, extract ion pair peaks according to Target List, perform ion ion matching and peak area calculation, and simultaneously determine and quantify peptides (Figure 13). If a standard peptide is added to the sample, the standard peptide can be used for retention time correction.
Figure 13. Skyline processes the complete process of DIA data
Figure 14. Statistical analysis and card value filtering using mProphet
Qualitative
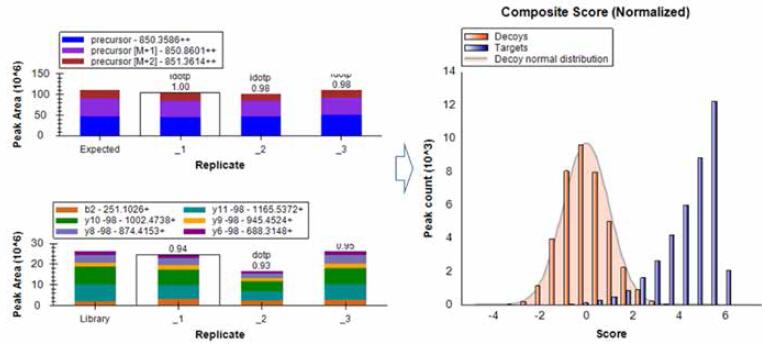
Statistical analysis of the spectral matching results using Skyline's embedded mProphet card value tool, taking into account factors such as dotp score, signal response, retention time, mass deviation, etc., and filtering the results to obtain highly reliable peptide qualitative results. (q < 0.01) (Fig. 14).
Quantitative
After qualitative card values ​​(q < 0.01), the peak area and CV value of all reliable ion pairs are finally obtained. The results are exported in Excel spreadsheet format, and the peak area is quantified using CV < 20% ions to complete the DIA analysis. Work (Figure 15).
Figure 15. Obtain ion pair peak area, CV value, and calculate quantitative results
Seven, application examples
This application example is a large-scale proteomics and phosphorylation proteomics quantification experiment using the DIA method. Simultaneous quantification of 3597 high-confidence proteins (21710 peptides) in 200 ng Hela whole cell lysates in a 120-minute effective gradient with q < 0.01 and CV < 20%; and in the same experiment Under conditions, 11341 high-confidence rat phosphorylated peptides were simultaneously quantified. Experiments have confirmed that the DIA method has unparalleled quantitative performance, whether it is a routine quantitative proteomics experiment or a post-translational modification quantitative study.
Links: Large-Scale Proteome and Phosphoproteome Quantification by Data Independent Acquisition on Ultra-High Field Orbitrap Mass Spectrometers
Eight, literature
Nine, related products
Q Exactive Series Orbitrap Ultra High Resolution Mass Spectrometer
(Q Exactive, Q Exactive Plus, and Q Exactive HF)
UltiMate TM 3000 RSLCnano Nanoliter Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatograph
Orbitrap Fusion "Three in One" Series Orbitrap Ultra High Resolution Mass Spectrometer
Easy-nLC nanoliter ultra high performance liquid chromatography
Pierce TM Peptide Retention Time Calibration Mixture Standard Peptide Mixture (Catalog No. 88320 & 88321)
Ten, related software
Proteome Discoverer Proteomics Analysis Software
(http://portal.thermo-brims.com/)
Skylines data non-dependent acquisition analysis software
(Free, https://skyline.gs.washington.edu)
XI. More information
More DIA related information resources:
• Visit the Orbitrap official information website:
Planet Orbitrap (http://planetorbitrap.com/)
• Please pay attention to the Orbitrap Proteomics WeChat public number:
Orbitrap Group Club (MSOmics)
Foot Spa Machine With Heat
A Foot Spa Machine with heat is a device used to provide a relaxing and therapeutic foot massage. It usually has a basin filled with warm water and has various massage settings such as vibration, bubbles, and rollers. The heat function helps soothe tired and aching feet, while the massage setting provides a deep-tissue massage that helps improve circulation, reduce tension, and relieve pain. Some foot spas also come with removable attachments, such as pumice stones and brushes, for extra exfoliation and cleansing. Overall, a foot spa machine with heat is a great tool for anyone looking to pamper their feet and promote overall relaxation and wellness.
Foot Spa Machine With Heat,Bubble Foot Bath Massager,Foot Massage Machine,Pedicure Foot Spa Machine
Huaian Mimir Electric Appliance Co., LTD , https://www.mmfootbath.com