Leica Classroom | Analysis of the sharp weapon in scientific research - the focus of the article
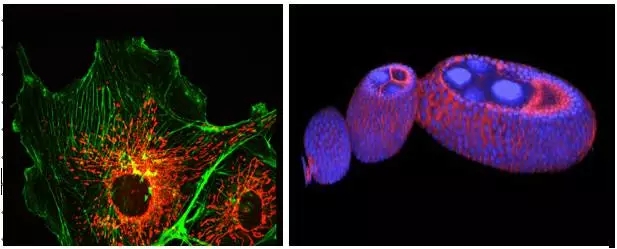
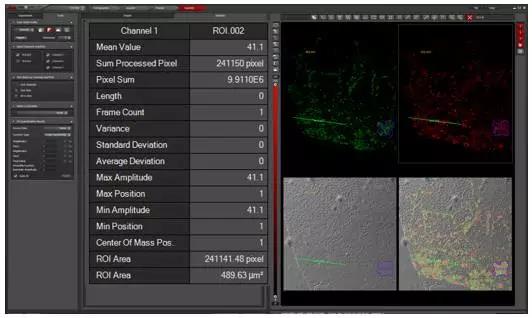
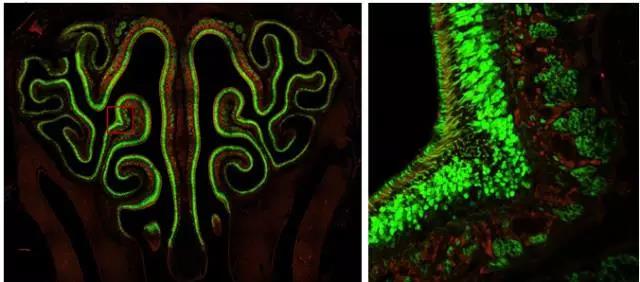
Are you still struggling to find better imaging techniques and tools on the battlefield of scientific research? Are you still struggling with the observed experimental phenomena to truly reflect the sample? Are you still upset about poor quality images and the ability to publish high quality papers? "Workers must first sharpen their tools when they want to do their best," and the focus will be on solving these problems for you. Compared with traditional wide-field imaging, confocal imaging, as a high-end microscopic imaging technique, has become a mainstream imaging method with its excellent imaging quality and 3D reconstruction capability. The next small series will take you into the world of confocal, to analyze the basic principles of confocal and its application in the field of biological research. Principle of confocal Confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) realizes point illumination and point detection by using an illumination pinhole placed behind the light source (laser) and a pinhole placed in front of the detector, and the light source is emitted through the illumination pinhole. The emitted light is focused at a point on the focal plane of the sample, and the fluorescence emitted by the point is imaged within the probe pinhole, and any emitted light outside the focal plane is blocked by the probe pinhole. Therefore, the fluorescence signal on the focal plane can be clearly obtained by confocal. The left and right sides of Figure 1 are the imaging paths of ordinary wide-field microscopes and confocal microscopes. Confocal microscopes use point detection and point illumination to obtain high-resolution images. The computer displays the detected points on the computer screen in a dot-like manner, and the scanning system in the optical path scans the focal plane of the sample to produce a complete confocal image. As the stage moves up and down along the Z axis, a new layer of the sample is imaged on the display, so that a continuous photo-cut image (Z-stack) of different layers of the sample can be obtained, and the sample can be accurately obtained through three-dimensional reconstruction. Three-dimensional information. Figure 2 Left: Point scan and Z-axis layer-cut mode of confocal microscopy; Right: Three-dimensional reconstruction of retinal neurons by confocal microscopy. Confocal application Compared with ordinary wide-field imaging, confocal can obtain high-resolution and high-definition three-dimensional images, so its application range is wider. Next, Xiaobian will introduce some important applications of confocal microscopy in the field of biological research. Fluorescence localization and 3D reconstruction The most important application of laser confocal microscopy is the observation and three-dimensional reconstruction of fluorescence localization. By fluorescence localization observation, the localization of the protein of interest in the cell or tissue can be known, and the subcellular localization of the protein can be obtained by labeling the structure of the organelle or the cytoskeleton, and by two or more colors with other proteins. Dyeing can analyze the colocalization of two or more proteins. Figure 3 Left: Clear imaging of cell microfilament skeleton (green, phalloidin) and mitochondria (red, mitrotracker) structure by confocal microscopy; right: three-dimensional reconstruction of Drosophila egg structure by confocal microscopy. Confocal imaging of the sample by point scanning, through the continuous movement of the Z-axis to achieve three-dimensional layer cutting of the sample and three-dimensional reconstruction of the sample to obtain accurate three-dimensional information (called "cell CT"), which can be more accurately in Z Analyze the localization of proteins on the axis. Fluorescence quantification and colocalization analysis If you want to quantify the fluorescence signal of a sample, you can easily do this with the Leica Confocal Microscope operating software, which is quick and easy. Figure 4 Quantification of the fluorescence signal by confocal software: Select the quantify-intensity-stack profile option, select the area to be analyzed through the ROI tool box, and display all the information of the selected area in the middle of the window, including the fluorescence channel and the average fluorescence. If you want to perform co-localization analysis on two or more signals, our software should be comfortable. Figure 5: Co-localization of fluorescence signals by confocal software: Select the quantify-colocalization option, select the area to be analyzed through the ROI tool box, and display the co-localization parameters of the selected two channels in the middle of the window, including the Pearson coefficient. Positioning ratio, etc. Multi-point scanning and puzzle What if your sample needs to take a large field of view while still needing high resolution? Don't worry, our software has an automatic puzzle function, you only need to set the two endpoints on the diagonal of the captured field of view, the software will be The calculations are automatically performed and automatic jigsaw shooting is performed. Similarly, if you don't need a puzzle, you only need to shoot more, and our software can easily do it for you. Figure 6 Auto jigsaw (left) and multi-point imaging (right) mode. Figure 7. Large-field high-resolution puzzle of the nasal layer of the mouse. Left: 48-view automatic puzzle (40x objective), right: zoom in on the selected area in the left image. Living imaging Confocal imaging not only images fixed samples, but also imaging live or tissue samples. It is easy to shoot as long as you set the relevant parameters. Of course, the conditions for maintaining sample activity during live photography are guaranteed, such as cell culture temperature, humidity, and carbon dioxide concentration, which can be easily achieved by selecting confocal microscope related accessories. This way you can track life processes such as cell proliferation, cell movement, cytoskeletal dynamics, and intracellular calcium signal changes through live imaging. Https://v.qq.com/iframe/preview.html?vid=p0377nymwzq Video 1 Confocal in vivo imaging of microtubule structures in COS7 cells for 5 minutes with a time interval of 5 seconds. Advanced application a. Spectral measurement The excitation and emission spectra of fluorescent proteins/dyes are particularly important when developing new fluorescent proteins/dyes or imaging autofluorescence samples such as plant leaves. Fluorescent protein/dye emission spectra can be easily scanned by confocal, and with the latest white lasers, simultaneous scanning of fluorescent protein/dye excitation and emission spectra can be easily done in minutes. Figure 8. Simultaneous scanning of the excitation and emission spectra of a six-color fluorescent bead sample by a white laser. b. FRAP (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching) The high-intensity laser is used to illuminate a certain region of the cell to photo-quench the fluorescent molecules in the region, and the non-quenched fluorescent molecules around the region will diffuse to the illuminated region at a certain rate, which can be directly detected by laser scanning confocal microscopy. The diffusion rate is measured to study biofilm fluidity, cytoskeletal dynamics, intracellular and intercellular material exchange. Figure 9 Fluorescence bleaching recovery technology (FRAP implementation process. c. FRET (Förster resonance energy transfer) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer occurs when the distance between the donor fluorescent molecule and the acceptor fluorescent molecule is sufficiently close and the emission spectrum of the donor overlaps with the absorption spectrum of the acceptor (within 10 nm). When the donor molecule absorbs a photon of a certain frequency and is excited to a higher electron energy state, the phenomenon of energy transfer to the adjacent acceptor molecule is achieved by resonance before the electron returns to the ground state. After FRET occurs, the fluorescence intensity of the donor is much lower than when it is present alone, and the fluorescence emitted by the acceptor is greatly enhanced. The interaction between molecules and the folding and conformational changes of molecules can be detected by FRET. Figure 10. Principle of fluorescence resonance energy transfer technique (FRET). The above advanced functions can be quickly implemented by selecting the corresponding module in the shooting software. summary Confocal microscopy, as a sharp weapon in scientific research, is far more than the above mentioned. Leica TCS SP8 X, a new generation of top-level confocal microscopes from Leica, is equipped with a white laser (a unique AOBS spectroscopic system), a prismatic spectroscopic slit detection system, an AFC autofocus device, and an ultra-high sensitivity detector HyD (with white laser High-resolution and high-resolution gated imaging), Hyvolution image processing software (up to 130nm high resolution by deconvolution processing), etc., can easily implement all of the above applications. At the same time, its powerful scalability makes SP8 easy to upgrade to STED ultra-high resolution microscope, MP multi-photon imaging system, Hi speed high-speed scanning system, etc. to achieve more powerful applications, it can be said that SP8 X confocal microscope as a scientific research The sharp weapon of the world is well deserved. Fingerprint Recognition Time Attendance Fingerprint Recognition Time Attendance,Employee Fingerprint Attendance Machine,Wall Mounted Fingerprint Attendance Machine,Fingerprint Attendance Equipment Chongqing Huifan Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.hfsecuritytech.com



(Courtesy: Dr. Yasushi Okada, University of Tokyo) 


