TMB marker function is recognized in a variety of cancer types
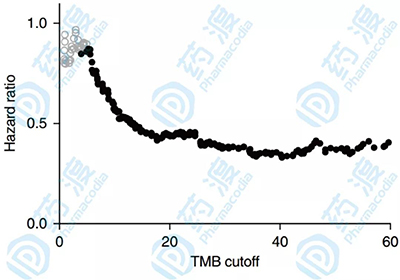
TMB marker function is recognized in a variety of cancer types March 01, 2019 Source: Yaodu The immune system plays a very important role in the process of tumor monitoring and clearance. The immune escape of tumor cells with the help of various mechanisms is considered to be one of the signs of cancer progression. As an important representative of immunotherapy, Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) is very beneficial for some patients with metastatic cancer, but predictive biomarkers are often needed to diagnose patients. Since the close relationship between tumor mutation load (TMB) and the benefits of immunotherapy has been revealed, research around TMB has become more and more abundant. Last October, the US NCCN (Comprehensive Cancer Network) officially included TMB in the guidelines for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The latest issue of Nature Genetics published a research article on TMB, which was used as a marker for immunotherapy. The "real hammer". The immune response process in the tumor microenvironment (picture from reference article 3) TMB has been used as a marker in clinical practice. High mutation load TMB and clinical benefit have been observed in the treatment of melanoma with CTLA-4 inhibitor and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor in melanoma, bladder cancer and NSCLC. Relevance. However, the clinical sample of TMB and survival rate after ICI treatment is small. It is not clear whether TMB has predictive clinical benefits of various cancers. It is not clear that this benefit will exceed the clinical specific test population. Whether it is still valid afterwards. To obtain more extensive data, the latest study included 1,662 clinical and genomic data from ICI for advanced cancer and 5,371 patients without ICI, and a new generation of targeted sequencing technology, MSK, for these patients. IMPACT. In all patients, high TMB (average tumor tissue mean value of approximately 20%) was positively correlated with better overall survival (OS), demonstrating a correlation between elevated TMB and increased survival in most cancers. . The relationship between threshold and death hazard ratio of different cancer TMB (image from reference article 2) The distribution of TMB levels in different cancer types (image from reference article 2) This stratified study is more conducive to the observation of the association of OS and TMB in different cancer types, although the impact on individual cancers (such as gliomas) may not be statistically significant due to sample size, but almost all types of cancer A high trend of high TMB and overall overall survival was observed, suggesting that the relationship between TMB and increased survival after ICI may be present in most cancer types. TMB acts as a continuous variable in many cancer histologies, and similar marker association trends are observed in longer OS. Consistent with improvements in OS, there is a similar correlation between TMB and ICI's objective response rate (ORR) or PFS in types such as NSCLC, melanoma, esophageal cancer, head and neck cancer, and renal cell carcinoma. Correlation between TMB level and overall survival (image from reference article 2) The researchers also performed MSK-IMPACT sequencing on 5,371 patients with metastatic cancer who did not receive ICI. In these patients, elevated TMB was not associated with increased OS. This ruled out that this positive association between TMB and patient survival is only due to differences in TMB between prognostic patients, and is not possible with ICI treatment. Given the potential toxicity of immunotherapy and the highly variable response to ICI, as well as the enormous economic cost of such therapies, there is an urgent need for positive or negative predictive biomarkers that can be used to predict ICI administration. Positive predictions can correctly determine which patients are able to produce a therapeutic response; negative predictions are used to determine which patients are not benefiting from current therapies. Biomarkers can be used to group patients with single or combination medications, or to decide on the use of immunotherapy for first-line and salvage treatments in different patient groups, or to use alternative therapies to avoid unnecessary toxicity. In addition to TMB, PD-L1 expression, lymphocyte infiltration, T cell receptor clonality, peripheral blood markers, immune-related gene expression, and multiplex immunohistochemistry have been demonstrated to have immunotherapeutic biomarkers. Wait, let's briefly introduce it below. Reference article: Electrical Fire Monitoring System Electrical Fire Monitoring System,Electrical Fire Monitoring Detector,Combined Fire Monitoring Detector,Combined Electrical Fire Detector LIAONING YINGKOU TIANCHENG FIRE PROTECTION EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD , https://www.tcfiretech.com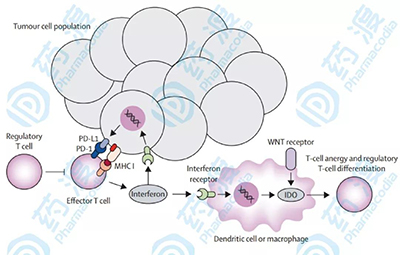
In addition, the study also performed a differential analysis of each cancer type, with the top 20% of the mutation load in each histology being the TMB high group of the cancer type. The reason for this is that TMB is distributed differently in different histologies, and there is a significant difference in the top 20% threshold for each type of cancer TMB, which means that it is impossible to have a common threshold definition of “what is high TMB†to predict ICI at all. Clinical benefits in the type of cancer. The difference in TMB between different tumor histology and the difference in ICI response threshold is likely due to the tumor microenvironment, including monoclonal immune penetration, immune cell rejection, human leukocyte antigen genotypic changes, and expression levels of checkpoint molecules. factor. 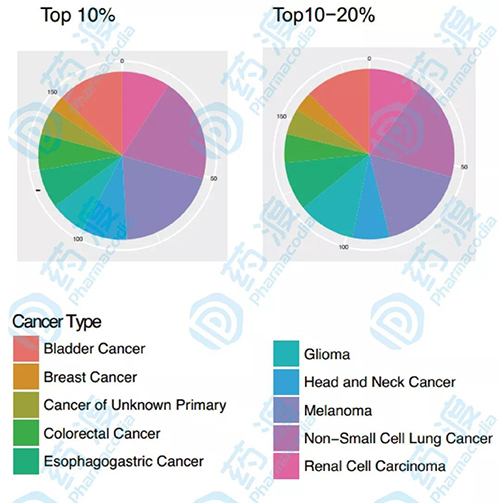
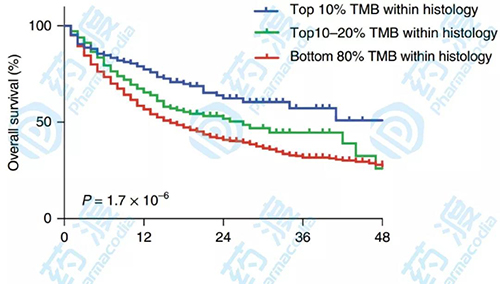
This research solves several important basic problems in tumor immunology: First, it is verified that the mutation load can be used to predict the survival rate of patients receiving anti-CTLA-4 or anti-PD-1 treatment. Second, the study used the largest-scale patient genomic data to date with ICI treatment, which quantified the clinical effects of TMB and demonstrated a sustained correlation between higher TMB and higher OS. Finally, the study found that the definition of “high†TMB varies from cancer to cancer, and it is difficult to predict the likelihood that all cancer patients will benefit from ICI with a common threshold. In conclusion, this finding re-emphasizes the reliability of TMB as a predictive biomarker with important clinical value. 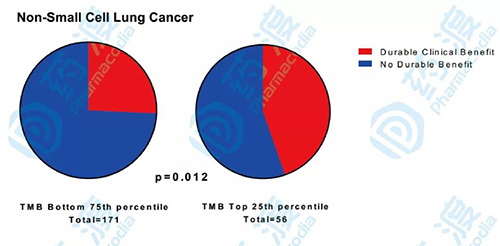
Clinical benefit prediction of TMB as a marker for ICI treatment of NSCLC (image from reference article 2)
1. PD-L1 expression was found in a phase I clinical study of Nivolumab for melanoma, NSCLC, renal cell carcinoma, prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer. It can be used as an anti-PD-1 by detecting PD-L1 expression in tumor cells. Biomarkers for PD-L1 treatment. 5% was set as the PD-L1 positive threshold for tumor cells, and 9 (36%) of the 25 PD-L1 positive patients had ORR for Nivolumab, and no negative patients showed ORR, in patients with advanced melanoma and NSCLC. The PFS and OS were also significantly improved in the middle-positive group compared with the negative group, and the FDA has approved the PD-L1 companion diagnosis for the treatment of advanced NSCLC and bladder cancer. However, due to the regulation of PD-L1 expression and the microenvironment of the tumor, the expression of PD-L1 has different sampling time, individual differences, and even intratumoral heterogeneity, and its negative predictive effect is much lower.
Despite these limitations, PD-L1 expression plays an important role in immunotherapeutic determination of beneficiary patient populations, especially in relevant clinical trials, ensuring that the average distribution of PD-L1-positive tumor patients in the comparison cohort is necessary. It is possible to avoid experimental deviations introduced by biological differences.
2. Lymphocyte infiltration levels Retrospective studies of many cancers have found that lymphocyte infiltration is associated with patient survival, and ectopic lymphoid structures are better found in solid tumor colonies such as colorectal cancer and melanoma. Predict the survival of patients. For example, patients with a high degree of tumor infiltration have a longer PFS and OS than patients with stage III chemoradiotherapy with a lower degree of CD8+ tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. The underlying mechanism of this degree of lymphocyte infiltration is thought to be capable of stimulating an autoimmune response or a T cell inflammatory tumor phenotype, improving disease control through an immune mechanism, and thus acting as a prognostic biomarker.
3. T cell receptor cloning studies found that tumor cell lymphocyte infiltrating T cell receptors target tumor-specific immune responses, which are related to the clinical response of Pembrolizumab. The results indicate that baseline T cell receptor clonality is associated with tumor infiltrating lymphocyte density. Not very sexual. When infiltrating lymphocytes limit the specific cloning of tumor antigens by T cell receptors, even patients with low tumor infiltrating lymphocytes can still benefit from anti-PD-1 therapy. Of course, this hypothesis needs to be further validated from a large number of clinical trials, and it may be necessary to identify an identifiable tumor antigen before the method can be applied to biomarkers.
4. Peripheral blood markers The advantage of peripheral blood markers lies in the non-invasive sample collection method. Although some correlations between these markers and clinical efficacy have been studied, there is no such marker that has truly “landed†therapy. Predictive. Taking Ipilimumab as an example, relevant clinical studies have found that the following indicators are related to PFS in patients, including low absolute neutrophil counts (< 7500 cells/μL), low proportion of neutrophil lymphocytes (< 3), absolute mononuclear Low cell count (< 650 cells/μL), low frequency myeloid suppressor cells (<5.1%), high frequency FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (≥1.5%), high frequency lymphocytes (≥10.5%) ), as well as high eosinophil counts (≥50 cells/μL), some similar results were found in anti-PD-1 treatment studies. In addition, the assessment of the number of peripheral T cells, particularly the T cell receptor gene sequence or reactivity to new antigens, can also serve as a predictive biomarker.
5. Immunologically related gene expression The generous expression of an innate or adaptive immune response in the tumor microenvironment can be used to effectively predict the clinical benefit of ICI therapy. A phase II clinical retrospective analysis of Ipilimumab in patients with advanced melanoma demonstrated that gene expression profiling is indeed a useful predictor of biomarkers. The researchers extracted 50 total RNA from pre-treatment tumor biopsy specimens and analyzed the patients. The patients were divided into two groups: clinical response and non-response. The path analysis of the genes with significant differences between the two groups revealed an associated inflammatory response. The expression of 22 immune-related genes was increased by at least 2.5-fold, including cytotoxic T cells (such as CD8A, granzyme B, perforin I), Th1 cytokines or chemokines, MHC class II and other immune-related genes ( Markers such as NKG7 and IDO1) are associated with OS prolongation.
6. Multiplex immunohistochemistry Direct evaluation of tumor and immune cell phenotypes and their spatial relationships by multiple immunohistochemistry techniques provides information on the immune status of tumor microenvironments, which can be used as a complement to gene expression profiles. This involves the continuous staining of tumor sections with a single primary antibody to obtain the protein of interest and detection by chromogenic or immunofluorescence methods. This multispectral method has great potential in clinical applications. By establishing a multi-spectral immunohistochemistry platform, CD3, CD8, FoxP3, CD163 and PD-L1 on melanoma slides were analyzed to predict which patients could successfully generate tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and select appropriate cell therapy. The presence of CD8+ T cells alone is not sufficient to predict successful growth of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, but the ratio of CD8+ T cells to CD3+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells is closely related to the successful growth of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. The addition of PD-L1+ increased the negative predictive value by 100%, and this method can also be applied to other immunotherapies.
7. Marker combination strategy Combining two or more marker strategies to capture the tumor microenvironment immune status can be more effective for ICI treatment. Taking PD-L1 expression and lymphocyte infiltration as an example, the two may be opposite in tumor cells, and the tumor infiltrating lymphocyte count is lower when PD-L1 expression is higher, and vice versa. In this case, anti-PD The clinical response of -1 or anti-PD-L1 monotherapy may be lower, and only PD-L1 expression or tumor infiltrating lymphocyte density as biomarkers may produce erroneous predictions. Similarly, not all high-mutation or new antigen-loaded tumors exhibit "innate" immunity, which is considered to be one of the prerequisites for immunotherapy. There are also a variety of concurrent immunosuppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment, including CTLA-4, PD-L2, LAG3, IDO1, and IL-10, which may become important targets of recognition with the advent of new combination therapy strategies.
[1]BMS Withdraws Application for Nivolumab/Ipilimumab in TMB-High NSCLC.
[2]Tumor mutational load predicts survival after immunotherapy across multiple cancer types.
[3]Predictive biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitorbased immunotherapy.
[4]Approaches to treat immune hot, altered and cold trumors with combination immunotherapies.