Application of emulsifier to improve digestibility of feed for weaned piglets
Because of the small amount of feed intake, newborn piglets have insufficient nutrient intake, especially energy, which affects the healthy growth of piglets. In order to improve the production performance of piglets, pigs and e-net users suggested that a method of adding fat to the feed to increase the energy concentration of the feed can be adopted. However, since lactating piglets cannot release emulsifiers for digesting and utilizing fat, the application of fat in actual production is limited. To this end, animal husbandry experts in the United States studied the use of chemical emulsifiers in feed for piglets. The trial used 17-21-day-old weaned piglets, which consist of corn, soybean cake, whey powder, skim milk powder, antibiotics, fat and other nutrients. Soybean oil, coconut oil, beef tallow, and lard oil were used as the four fat sources and added in the diet of weaned piglets at 10%. The emulsifiers were lecithin and cephalin. The added amounts were 10% and 30% of the fats added. %. The test results showed that the digestibility of dry matter, total energy and fat in the soybean oil and coconut oil supplemented groups were higher than those in the beef and lard oil groups. This is mainly due to the difference in the length of various fatty carbon chains and the degree of unsaturation of fatty acids, and the difference in the amount of fat as a source of nitrogen is not much different. When lecithin and cephalin were added to the diet containing tallow (adding 10% of the amount of tallow), the digestibility of fat in the diet increased from 80.9% to 88.4% and 83.9%, respectively. Adding emulsifiers to lard-containing diets, on the other hand, reduces fat digestibility. During the 35-day lactation period, neither soy oil nor the beef group increased the weight gain of the piglets, but the feed utilization rate was significantly higher than the control group without fats. Recommended reading: Emulsifier OP-10: http:// Lithium Carbonate CAS No.554-13-2 Lithium Carbonate Basic Information
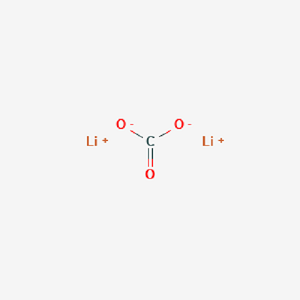
Lithium Carbonate Structure
Lithium Carbonate,Lithium Carbonate Dosage,Uses For Lithium Carbonate,Lithium Carbonate Uses,Lithium Carbonate Side Effects ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com
CAS: 554-13-2
MF: CLi2O3
MW: 73.89
EINECS: 209-062-5
Mol File: 554-13-2.mol
Melting point 720 °C
Boiling point 1342 °C(lit.)
density 2.11 g/mL at 25 °C
Fp 1310°C
storage temp. Store at +5°C to +30°C.
solubility 13g/l
form wire
Specific Gravity 2.11
color White
PH 10-11 (5g/l, H2O, 20℃)
Water Solubility 13 g/L (20 ºC)